Understanding the Snowflake Breach
Snowflake, a leading cloud-based data warehousing company, recently faced a wave of attacks targeting its enterprise customers, resulting in the leakage of millions of sensitive records. Here’s a closer look at what happened and how companies can protect themselves.
Attack Path and Methodology
The attack spree against Snowflake customers began in mid-April 2024 and was officially acknowledged by Snowflake on May 23, 2024.
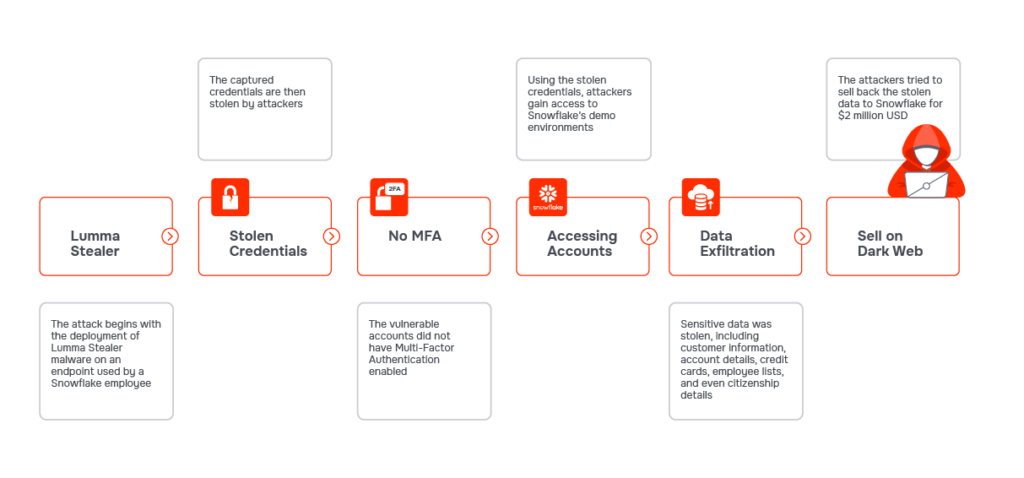
The attack did not stem from a vulnerability within Snowflake’s platform. Instead, it was an identity and misconfiguration-based attack that exploited weak identity and access controls, as well as the absence of multifactor authentication. Here’s a breakdown of the attack path:
- Initial Compromise: Attackers used credentials stolen by info-stealing malware, probably using Lumma Stealer malware.
- Accessing Accounts: The attackers gained access to Snowflake environments using these stolen credentials. Notably, many of the compromised accounts lacked multi-factor authentication (MFA), making them easy targets.
- Data Exfiltration and Extortion: Once inside, the attackers stole data from the compromised databases. They further pressured organizations by warning they would sell the stolen data on the dark web if their demands were not met.
- Widespread Impact: The attack campaign affected several major companies, leading to high-alert advisories from cybersecurity authorities like the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA).
Security Recommendations
In response to these incidents, Snowflake and the cybersecurity community have issued several recommendations to mitigate such identity-based threats:
- Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing MFA across all accounts is crucial to prevent unauthorized access, even if credentials are compromised.
- Set Up Network Policy Rules: Restrict network access to trusted locations and ensure only authorized users can access critical systems or sensitive SaaS accounts.
- Reset and Rotate Credentials: Regularly update and rotate credentials to limit the potential damage from stolen credentials. This will reduce the time window during which stolen credentials can be used by malicious actors, disrupt attackers ongoing access and reduce the ‘Risk of Credential Stuffing Attacks’ (Credential stuffing attacks involve using stolen username and password combinations from one breach to gain access to accounts on other services).
- Monitor for Unusual Activity: Continuously monitor for signs of unusual user activity, such as unauthorized access attempts from unfamiliar IP addresses.
How Suridata Can Help
Suridata offers robust features to help organizations secure their SaaS environment, including Snowflake. Here’s how Suridata can assist:
- Comprehensive Security Analysis: Suridata conducts comprehensive security assessments of SaaS configurations, identifying potential weaknesses and exposures. Preventive measures that can be taken include:
- Restrict public access and enforce IP whitelisting.
- Restriction of network policies that are too permissive.
- Identify users not enrolled in MFA and enforce mandatory enrollment.
- Identity and Access Management: Suridata enhances identity and access management by ensuring that authentication mechanisms, including MFA, are in place and properly configured for all users. It also detects user anomalies, that can provide insights into suspicious activities, potentially preventing threats before they can escalate.
- On-demand User Remediation: Suridata offers remediation capabilities, enabling organizations to swiftly address user misconfigurations and enforce best practices across the Snowflake environment. From Suridata’s platform, risky users can be blocked from an application, their permissions can be revoked, or they can be deleted.
Conclusion
The recent attacks on Snowflake customers highlight the critical importance of robust identity and access controls in the SaaS environment. By implementing preventive measures, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to similar identity-based threats. Suridata conducts thorough security checks of misconfigurations, identifying potential weaknesses. Key preventive recommendations include:
- Implementing network policies that restrict access based on the user’s IP address.
- Identifying and tightening overly permissive network policies to ensure access is granted only to authorized users.
- Identifying users not enrolled with MFA and ensuring they are promptly secured.
- Not sure if you are using Snowflake? Suridata offers free application scanning to help you identify and prevent attacks in your SaaS environments.
Co-Founder & CPO
